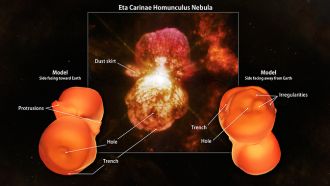
 In the middle of the 19th century, the massive binary system Eta Carinae underwent an eruption that ejected at least 10 times the sun's mass and made it the second-brightest star in the sky. Now, a team of astronomers has used extensive new observations to create the first high-resolution 3-D model of the expanding cloud produced by this outburst.
In the middle of the 19th century, the massive binary system Eta Carinae underwent an eruption that ejected at least 10 times the sun's mass and made it the second-brightest star in the sky. Now, a team of astronomers has used extensive new observations to create the first high-resolution 3-D model of the expanding cloud produced by this outburst.
"Our model indicates that this vast shell of gas and dust has a more complex origin than is generally assumed," said Thomas Madura, a NASA Postdoctoral Program fellow at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and a member of the study team. "For the first time, we see evidence suggesting that intense interactions between the stars in the central binary played a significant role in sculpting the nebula we see today."
Read the full press release at nasa.gov

